Below the 1000+ Questions with detail solution on Air pollution of Environmental Engineering subject, which were asked in various competitive exam of Civil Engineer for various posts.
Question 1.
Which analytical method is commonly used to measure and analyze particulate matter in ambient air samples?
Previously Asked in : SKUAST Civil Engineer Civil (post code: 71) ||
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
High-Performance Liquid Spectrometry (HPLC)
Differential Optical Absorption
Ga Chromatography-Mass (GC MS)
DOAS
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is correct
Detailed Solution :
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is one of the most useful techniques of examination of PM in environmental samples involving air.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) allows to study the form of particles and their elemental content.
This method has an advantage in producing images that are of high resolution for both the dimensions of the particles and their surface structures.
In the case of Scanning Electron Microscopy, it utilizes the appropriate focused electron beam to bombard the particulate matter as its distinguishing vessel.
This channel produces secondary electrons from the particulate matter which is accessed by the image of the sample that looks for the interaction with the particulate matter. Additionally, energy dispersive x-ray
Question 2.
Which of the following gases is responsible for acid rain?
Previously Asked in : SSC JE 2011 Shift-1 ||
VOC
NOX
SO2
CH4
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option SO2 is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Natural rainfalls through unpolluted is slightly acidic, with the PH just less than 7
However, when the environment is polluted with primary pollutant, like SO2 and NOx, the resultant rainfalls tends to become more and more acidic, with the increasing concentration of these pollutants.
The acidity in rain water is caused due to the formation of secondary pollutant like H2SO4, HNO3 etc due to the reaction of water vapour with SO2, NOx and HCL gas.
Note:
- The greater is the concentration of these primary pollutants, the greater would be the acidity and hence lesser the PH value of the resultant rain.
- It has been specified that when the PH of the rain water falls to 5.6 or below, the rain specified as acidic.
- CH4, CO are green house gases.
Question 3.
___ is a primary air pollutant.
Previously Asked in : DSSSB AE 27.09.2021
Formaldehyde
Sulphur dioxide
Ozone
Sulphuric acid
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Sulphur dioxide is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Primary pollutants are emitted from natural sources directly into the atmosphere. Ex- ammonia, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and CO etc.
Secondary Pollutant result from the chemical reaction or physical interactions between the primary pollutants, Ex- Ozone, acid rain, PAN, photo chemical and smog.
Question 4.
Identify the one which does not belong to the category of Secondary air pollutant?
Previously Asked in : DSSSB AE 26.09.2021
PAN (Peroxy Acetyl Nitrate)
Oxides of Nitrogen
Ozone
Photo chemical smog
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Oxides of Nitrogen is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Primary pollutants are emitted from natural sources directly into the atmosphere. Ex- ammonia, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and CO etc.
Secondary Pollutant result from the chemical reaction or physical interactions between the primary pollutants, Ex- Ozone, acid rain, PAN, photo chemical and smog.
Question 5.
The global warming is caused mainly by :
Previously Asked in : SSC JE 2014 Shift-2 ||
O2
NOX
SO2
Co2
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Co2 is correct
Detailed Explanation :
CO2 is considered to be the major green house gas, as it is responsible for about 60% of the total green house effect caused by all the green house gases.
- Other green house gases are: CH4, NOx and chlorofluoro carbon.
- NOx and SOx are the gases which cause acid rain.
Global warming potential:
Global warming potential (GWP) is a relative measure of amount of heat absorbed by any greenhouse gas with respect to carbon dioxide.
It compares the potential impact of different greenhouse gases b calculating the amount of heat trapped by one kilogram of any green house gas compared to the amount of heat trapped by one kilogram of CO2.
The GWP depends on the following factors:
- The absorption of infrared radiation by a give greenhouse gases.
- The absorption band wavelength of gas.
- The atmospheric lifetime of the gases.
| Green House gas | How it is Produced | 100 yr GWP |
| Carbon dioxide CO2 | burning of fossil fuels, solid wastes | 1 |
| Methane CH4 | Anaerobic decay of organic waste | 25 |
| Nitrous oxide N2O | Agricultural and industrial activities | 298 |
| Hydrofluoro-carbons e.g HFC-23 | Liquid coolants | 14800 |
| Perfluoro-carbons e.g CF4 | Refrigerant, electronic industry and aluminium industry | 6500 |
| Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) | Insulator in electronics and mangnesium industry | 22800 |
Learn more : Important Mcqs on Strength of material with detail Solution
Learn more : 1000+ Environmental Engineering MCQs with Answer
Question 6.
Green house effect of CO2 is
Previously Asked in : SSC JE 01 Mar 2017 Shift-1 ||
Permitting the outside solar radiation to reach the ground but preventing terrestrial radiation from the ground into the space
Permitting the solar radiation of short length and reradiated terrestrial heat of long wave length
Reflecting the heat rays into the space there by keeping the temperature of earth unaffected
Causing absorption of heat from troposphere and there by decreasing the temperature of earth with increase in CO2 concentration
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Permitting the outside solar radiation to reach the ground but preventing terrestrial radiation from the ground into the space is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Earth receives energy from the sun in the form of ultraviolet, visible and infrared radiation.
About 26% of the incoming solar energy is reflected to space by the atmosphere and clouds.
Most of the remaining energy is absorbed at the surface of earth.
Because the earth’s surface is colder than the sun, it radiates at wavelengths that are much longer than the wavelengths that were absorbed.
Question 7.
The device used for the easy separation dry dust of 10 to 100 μ m size is
Previously Asked in : SSC JE 01 MAR 2017 Shift-2 ||
Cyclone
Gravity settling chamber
Bag filter
Scrubber
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Cyclone is correct
Detailed Explanation :
A cyclone collectors consists of a cylindrical shell, conical base, dust hopper and an inlet where the dust-laden gas enters tangentially
A cyclone collector is a closed chamber in which the inlet velocity of the gas (smokes) is transformed into a spining vortex, which helps to throw out the particles under the generated centrifugal force.
The particles then side down the chamber walls into the hopper from where they come out.
The operating or separating efficiency of a cyclone depends on the magnitude of the centrifugal force exerted on the particles.
The greater the centrifugal force the greater the separating efficiency.
Large dia cyclone collectors have good collection efficiencies for a particles 40 to 50 μm in diameter.
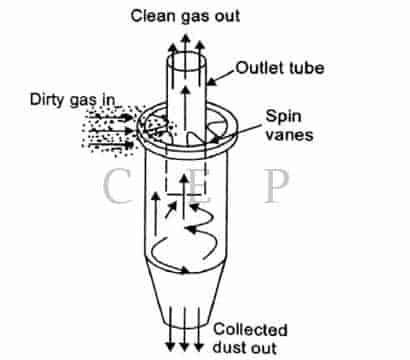
Method of removal particulate matter
| Equipment | Out size removed | Remarks |
| 1. Gravitational settling chamber | Only large size particles are separated out (>50 μm) | Simple to design and maintain and has low collection efficiency require large space for installation. Low pressure loss. |
| 2. Cyclone separators | Large dia cyclone efficient for 40-50 μm small dia cyclone (dia <23 cm) efficient of 15 ot 20 μm for particles sizes from 5 to 10 μm (Removal 90% efficiency) | Relatively inexpensive, simple to design and maintain. Require less floor area. Low to moderate pressure loss. |
| 3. Fabric filter | Filter bag usually tubular or envelope shaped are capable of removing most particle as 0.5 μm and grill removed substantial quantity of particles as smell as 0.1 μm | Fabric filters can give high efficiency, and can even remove very small particles in dry state. High temperature gases needs to be cooled. The flue gases must be dry to avoid condensation and clogging. The fabric is liable to chemical attack. |
| 4. Electrostatic precipitator | Very small particles also, wet and dry can be easily trapped. More than 99% efficiency can be achieved in their functioning. | It is one of the most widely used device for controlling particulate emission at industrial installations ranging from power plants, cement and paper mils. |
| 5. Wet scrubbers a) Venturi Scrubbers b) Spray tower c) Wet cycone scrubbers | Most efficient for removing particulate matter in the size range of 0.5 to 5 μm. Gases and particulate contamination removal. 100% efficient for 100mm and 90%- 98% for 5-50μm. | It can efficiently remove gaseous as well as particulate contaminants. Low cost handling of large volume of gases. High efficiency than spray towers. |
Question 8.
In dealing with the problem of air pollution, gravitational settling chambers are generally used to remove large, abrasive particles from:
Previously Asked in : DSSSB AE 01 26.09.2021
Stack
Gas streams
Stack and ambient air
Ambient air
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Gas streams is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Gravity settling chambers:
This is a simple particulate collection device using the principle of gravity to settle the particulate matter in a gas stream passing through its long chamber.
Question 9.
Which of the following pollutants are responsible for the cause of SMOG?
Previously Asked in : WB AE(Envirnomental) 28 01 2021
From incinerators
Emissions from vehicles
Both incinerators and emissions from vehicles
None of the above
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Both incinerators and emissions from vehicles is correct
Detailed Explanation :
Photo chemical smog is caused by the interaction of some hydrocarbons and oxidents (mainly Nitrogen oxides) under the influence of sunlight giving rise to dangerous peroxy- acetyl nitrate (PAN) .
Modern smog (also called traffic smog). It is a pollutant derived from vechiclurar emission.
Coal induced smog consist of smoke, sulpher compound and fly ash.
Question 10.
Pollutant standards index (PSI) value in between 101-199 denotes the air quality as:
Previously Asked in : SSC JE 02 03 2017 (morning)
Good
Moderate
Unhealthy
Harardous
Answer (Detailed Solution Below)
Option Unhealthy is correct
Detailed Explanation :
The pollutant standard index or PSI, is a type of air quality index, which is a number used to indicate the level of pollutant in air.
PSI consider six air pollutant
- sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- particulate matter (PM10)
- Fine particulate matter (PM2.5)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Ozne
| PSI | Description | General Health effect |
| 0-50 | Good | None |
| 51-100 | Moderate | Few or more for the general |
| 101-200 | Unhealthy | Every one may being to experience health effect, members of sensitive groups may experience more serious health effect. |
| 201-300 | Unhealthy | Health warming of emergency condition. The entire population is more likely to be affected. |
| 301 + | Hazardous | Health alert every one may experience more serious health effect. |
Please Help us to make it error free. So if you found any kind of error/mistake, do report us by click here or drop a Mail @ admin@civilenggpro.com